
















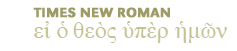
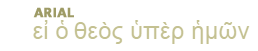

Moon:
heb. yareah, from its paleness (Ezr 6:15), and lebanah, the "white" (Sgs 6:10; Isa 24:23), was appointed by the Creator to be with the sun "for signs, and for seasons, and for days, and years" (Gen 1:14-16). A lunation was among the Jews the period of a month, and several of their festivals were held on the day of the new moon. It is frequently referred to along with the sun (Jos 10:12; Psa 72:5,7,17; 89:36,37; Ecc 12:2; Isa 24:23, etc.), and also by itself (Psa 8:3; 121:6).
The great brilliance of the moon in Eastern countries led to its being early an object of idolatrous worship (Deu 4:19; 17:3; Job 31:26), a form of idolatry against which the Jews were warned (Deu 4:19; 17:3). They, however, fell into this idolatry, and offered incense (2Ki 23:5; Jer 8:2), and also cakes of honey, to the moon (Jer 7:18; 44:17-19,25).
Moon:
moon (yareach; meaning obscure-probably "wanderer"; by some given as "paleness"; selene): The moon was very early worshipped by the nations of the Far East as a divinity or the representative of one or more deities. These deities were both masculine and feminine. In Assyria and Babylonia the most common name for the moon-god was Sin or Sen. In Babylonia he was also called Aku and Nannara. In Egypt the moon was representative of several deities, all masculine. The chief of these was Thoth the god of knowledge, so called because the moon was the measurer of time. Babylonia has, also, Aa, the goddess of the moon, as the consort of the sun, while her equivalent was known in Phoenicia as Ashtaroth-karnaim. This personification and worship of the moon among the nations who were neighbors to Palestine was but part of an elaborate Nature-worship found among these people. Nor was this worship always separated from Palestine by geographical lines. It crept into the thought and customs of the Hebrews and in a sense affected their religious conceptions and ceremonies. They fell into the habit of making direct homage to sun, moon and stars, as is evidenced by Job 31:26,27; Jer 44:17, and even Isa 8:18 (see CRESCENTS). Moses seems to have forewarned his people against the danger of this form of worship (De 4:19).
The actual worship of the moon and the idolatry consequent thereon seems to have touched the Hebrews, though this is disputed by some. It would seem difficult to explain 2Ki 21:3 upon any other supposition, and in 2Ki 23:4,5 we have a clear statement that Josiah put down the worship of the moon among the people and silenced the priests of this form of worship.
Certain forms of the adoration of the moon, or superstitious fear of baneful influences as coming from the moon, still abound in some sections of the world. In fact in nearly all sections modified forms of old superstitions still hold sway and yield but slowly to scientific knowledge.
The eclipses of the moon were naturally given a religious significance inasmuch as the Hebrew knowledge of them did not rise much above awe and wonder (Isa 13:10; Joe 2:31; Mt 24:29; Mr 13:24). Other passages causing interference with the constancy of the moon to foreshadow great events can be found in Jer 13:16; Eze 32:7,8; Re 8:12. An interesting passage and most difficult of interpretation is Re 12:1. It is frequently interpreted as a revelation in symbolism of the glory of the church clothed with the light and radiating the truth of God.
Written by C. E. Schenk
See ASTRONOMY
See ASTROLOGY
| 1 | Strong's Number: g4582 | Greek: selene |
Moon:
from selas, "brightness" (the Heb. words are yareach, "wandering," and lebanah, "white"), occurs in Mat 24:29; Mar 13:24; Luk 21:25; Act 2:20; 1Cr 15:41; Rev 6:12; 8:12; 12:1; 21:23. In Rev 12:1, "the moon under her feet" is suggestive of derived authority, just as her being clothed with the sun is suggestive of supreme authority; everything in the symbolism of the passage centers in Israel. In Rev 6:12 the similar symbolism of the sun and "moon" is suggestive of the supreme authority over the world, and of derived authority, at the time of the execution of Divine judgments upon nations at the close of the present age.
| 2 | Strong's Number: g3561 | Greek: neomenia | noumenia |
Moon:
denoting "a new moon" (neos, "new," men, "a month:" see MONTH), is used in Col 2:16, of a Jewish festival. Judaistic tradition added special features in the liturgy of the synagogue in connection with the observance of the first day of the month, the new "moon" time.
In the OT the RV has "new moon" for AV, "month" in Num 29:6; 1Sa 20:27; Hsa 5:7. For the connection with feast days see Lev 23:24; Num 10:10; 29:1; Psa 81:3.
Moon:
The moon held an important place in the kingdom of nature, as known to the Hebrews. Conjointly with the sun, it was appointed "for signs and for seasons, and for days and years;" though in this respect it exercised a more important influence, if by the "seasons" we understand the great religious festivals of the Jews, as is particularly stated in Psalm 104:19 and more at length in Ecclesiasticus 43:6-7. The worship of the moon prevailed extensively among the nations of the East, and under a variety of aspects. It was one of the only two deities which commanded the reverence of all the Egyptians. The worship of the heavenly bodies is referred to in Job 31:26, 27 and Moses directly warns the Jews against it (Deuteronomy 4:19). In the figurative language of Scripture, the moon is frequently noticed as presaging events of the greatest importance through the temporary or permanent withdrawal of its light (Isaiah 13:10; Joel 2:31; Matthew 24:29; Mark 13:24).
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
