
















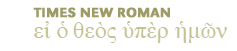
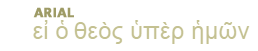

Plague:
a "stroke" of affliction, or disease. Sent as a divine chastisement (Num 11:33; 14:37; 16:46-49; 2Sa 24:21). Painful afflictions or diseases, (Lev 13:3,5,30; 1Ki 8:37), or severe calamity (Mar 5:29; Luk 7:21), or the judgment of God, so called (Exd 9:14). Plagues of Egypt were ten in number.
(1.) The river Nile was turned into blood, and the fish died, and the river stank, so that the Egyptians loathed to drink of the river (Exd 7:14-25).
(2.) The plague of frogs (Exd 8:1-15).
(3.) The plague of lice (Heb. kinnim, properly gnats or mosquitoes; Psa 78:45; 105:31), "out of the dust of the land" (Exd 8:16-19).
(4.) The plague of flies (Heb. arob, rendered by the LXX. dog-fly), Exd 8:21-24.
(5.) The murrain (Exd 9:1-7), or epidemic pestilence which carried off vast numbers of cattle in the field. Warning was given of its coming.
(6.) The sixth plague, of "boils and blains," like the third, was sent without warning (Exd 9:8-12). It is called (Deu 28:27) "the botch of Egypt," A.V.; but in R.V., "the boil of Egypt." "The magicians could not stand before Moses" because of it.
(7.) The plague of hail, with fire and thunder (Exd 9:13-33). Warning was given of its coming. (Psa 18:13; 105:32,33).
(8.) The plague of locusts, which covered the whole face of the earth, so that the land was darkened with them (Exd 10:12-15). The Hebrew name of this insect, arbeh, points to the "multitudinous" character of this visitation. Warning was given before this plague came.
(9.) After a short interval the plague of darkness succeeded that of the locusts; and it came without any special warning (Exd 10:21-29). The darkness covered "all the land of Egypt" to such an extent that "they saw not one another." It did not, however, extend to the land of Goshen.
(10.) The last and most fearful of these plagues was the death of the first-born of man and of beast (Exd 11:4,5; 12:29,30). The exact time of the visitation was announced, "about midnight", which would add to the horror of the infliction. Its extent also is specified, from the first-born of the king to the first-born of the humblest slave, and all the first-born of beasts. But from this plague the Hebrews were completely exempted. The Lord "put a difference" between them and the Egyptians. (See PASSOVER.)
Plague:
plag (negha‘, makkah, maggephah; mastix, plege): This word which occurs more than 120 times is applied, like pestilence, to such sudden outbursts of disease as are regarded in the light of divine visitations. It is used in the description of leprosy about 60 times in Le 13 and 14, as well as in De 24:8. In the poetical, prophetic and eschatological books it occurs about 20 times in the general sense of a punitive disaster. The Gospel references (Mr 3:10; 5:29,34; Lu 7:21) use the word as a synonym for disease.
The specific disease now named "plague" has been from the earliest historic times a frequent visitant to Palestine and Egypt. Indeed in the Southeast between Gaza and Bubastis it has occurred so frequently that it may almost be regarded as endemic. The suddenness of its attack, the shortness of its incubation period and the rapidity of its course give it the characters which of old have been associated with manifestations of divine anger. In the early days of an epidemic it is no infrequent occurrence that 60 per cent of those attacked die within three days. I have seen a case in which death took place ten hours after the first symptoms. In the filthy and insanitary houses of eastern towns, the disease spreads rapidly. In a recent epidemic in one village of 534 inhabitants 311 died within 21 days, and I once crossed the track of a party of pilgrims to Mecca of whom two-thirds died of plague on the road. Even with modern sanitary activity, it is very difficult to root it out, as our recent experiences in Hong Kong and India have shown.
Of the Biblical outbreaks that were not improbably bubonic plague, the first recorded is the slaughter of the firstborn in Egypt-the 10th plague. We have too little information to identify it (Ex 11:1). The Philistines, however, used the same name, negha‘, for the Egyptian plagues (1Sa 4:8) as is used in Ex. The next outbreak was at Kibroth-hataavah (Nu 11:33). This was synchronous with the phenomenal flight of quails, and if these were, as is probable, driven by the wind from the plague-stricken Serbonian region, they were equally probably the carriers of the infection. Experience in both India and China has shown that animals of very diverse kinds can carry germs of the disease. A third visitation fell on the spies who brought back an evil report (Nu 14:37). A fourth destroyed those who murmured at the destruction of Korah and his fellow-rebels (Nu 16:47). These may have been recrudescences of the infection brought by the quails. The fifth outbreak was that which followed the gross religious and moral defection at, Baal-peor (Nu 25:8,9,18; 26:1; 31:16; Jos 22:17; Ps 106:29,30). Here the disease was probably conveyed by the Moabites.
A later epidemic, which was probably of bubonic plague, was that which avenged the capture of the ark (1Sa 5:6). We read of the tumors which were probably the glandular enlargements characteristic of this disease; also that at the time there was a plague of rats (1Sa 6:5)-"mice," in our version, but the word is also used as the name of the rat. The cattle seem to have carried the plague to Beth-shemesh, as has been observed in more than one place in China (1Sa 6:19). Concerning the three days' pestilence that followed David's census (2Sa 24:15; 1Ch 21:12), see Josephus, Ant, VII, xiii, 3. The destruction of the army of Sennacherib may have been a sudden outbreak of plague (2Ki 19:35; Isa 37:36). It is perhaps worthy of note that in Herodotus' account of the destruction of this army (ii.141) he refers to the incursion of swarms of mice.
One of the latest prophetic mentions of plague is Ho 13:14, where the plague (debher, Septuagint dike) of death and the destruction (qaTabh, Septuagint kentron) of the grave are mentioned. From this passage Paul quotes his apostrophe at the end of 1Co 15:55, but the apostle correlates the sting (kentron) with death, and changes the dike into nikos.
Written by Alexander Macalister
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
