
















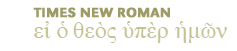
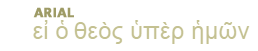

Prophet:
(Psa 45:1). This Hebrew word is the first and the most generally used for a prophet. In the time of Samuel another word, ro'eh, "seer", began to be used (1Sa 9:9). It occurs seven times in reference to Samuel. Afterwards another word, hozeh, "seer" (2Sa 24:11), was employed. In 1Ch 29:29 all these three words are used: "Samuel the seer (ro'eh), Nathan the prophet (nabi'), Gad the seer" (hozeh). In Jos 13:22 Balaam is called (Heb.) a kosem "diviner," a word used only of a false prophet.
The "prophet" proclaimed the message given to him, as the "seer" beheld the vision of God. (See Num 12:6, 8.) Thus a prophet was a spokesman for God; he spake in God's name and by his authority (Exd 7:1). He is the mouth by which God speaks to men (Jer 1:9; Isa 51:16), and hence what the prophet says is not of man but of God (2Pe 1:20,21; Hbr 3:7; Act 4:25; 28:25). Prophets were the immediate organs of God for the communication of his mind and will to men (Deu 18:18,19). The whole Word of God may in this general sense be spoken of as prophetic, inasmuch as it was written by men who received the revelation they communicated from God, no matter what its nature might be. The foretelling of future events was not a necessary but only an incidental part of the prophetic office. The great task assigned to the prophets whom God raised up among the people was "to correct moral and religious abuses, to proclaim the great moral and religious truths which are connected with the character of God, and which lie at the foundation of his government."
Any one being a spokesman for God to man might thus be called a prophet. Thus Enoch, Abraham, and the patriarchs, as bearers of God's message (Gen 20:7; Exd 7:1; Psa 105:15), as also Moses (Deu 18:15; 34:10; Hsa 12:13), are ranked among the prophets. The seventy elders of Israel (Num 11:16-29), "when the spirit rested upon them, prophesied;" Asaph and Jeduthun "prophesied with a harp" (1Ch 25:3). Miriam and Deborah were prophetesses (Exd 15:20; Jdg 4:4). The title thus has a general application to all who have messages from God to men.
But while the prophetic gift was thus exercised from the beginning, the prophetical order as such began with Samuel. Colleges, "schools of the prophets", were instituted for the training of prophets, who were constituted, a distinct order (1Sa 19:18-24; 2Ki 2:3,15; 4:38), which continued to the close of the Old Testament. Such "schools" were established at Ramah, Bethel, Gilgal, Gibeah, and Jericho. The "sons" or "disciples" of the prophets were young men (2Ki 5:22; 9:1,4) who lived together at these different "schools" (4:38-41). These young men were taught not only the rudiments of secular knowledge, but they were brought up to exercise the office of prophet, "to preach pure morality and the heart-felt worship of Jehovah, and to act along and co-ordinately with the priesthood and monarchy in guiding the state aright and checking all attempts at illegality and tyranny."
In New Testament times the prophetical office was continued. Our Lord is frequently spoken of as a prophet (Luk 13:33; 24:19). He was and is the great Prophet of the Church. There was also in the Church a distinct order of prophets (1Cr 12:28; Eph 2:20; 3:5), who made new revelations from God. They differed from the "teacher," whose office it was to impart truths already revealed.
Of the Old Testament prophets there are sixteen, whose prophecies form part of the inspired canon. These are divided into four groups:
(1.) The prophets of the northern kingdom (Israel), viz., Hosea, Amos, Joel, Jonah.
(2.) The prophets of Judah, viz., Isaiah, Jeremiah, Obadiah, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephaniah.
(3.) The prophets of Captivity, viz., Ezekiel and Daniel.
(4.) The prophets of the Restoration, viz., Haggai, Zechariah, and Malachi.
| 1 | Strong's Number: g4396 | Greek: prophetes |
Prophet:
"one who speaks forth or openly" (see PROPHECY, A), "a proclaimer of a divine message," denoted among the Greeks an interpreter of the oracles of the gods.
In the Sept. it is the translation of the word roeh, "a seer;" 1Sa 9:9, indicating that the "prophet" was one who had immediate intercourse with God. It also translates the word nabhi, meaning "either one in whom the message from God springs forth" or "one to whom anything is secretly communicated." Hence, in general, "the prophet" was one upon whom the Spirit of God rested, Num 11:17-29, one, to whom and through whom God speaks, Num 12:2; Amo 3:7, 8. In the case of the OT prophets their messages were very largely the proclamation of the Divine purposes of salvation and glory to be accomplished in the future; the "prophesying" of the NT "prophets" was both a preaching of the Divine counsels of grace already accomplished and the foretelling of the purposes of God in the future.
In the NT the word is used
(a) of "the OT prophets," e.g., Mat 5:12; Mar 6:15; Luk 4:27; Jhn 8:52; Rom 11:3;
(b) of "prophets in general," e.g., Mat 10:41; 21:46; Mar 6:4;
(c) of "John the Baptist," Mat 21:26; Luk 1:76;
(d) of "prophets in the churches," e.g., Act 13:1; 15:32; 21:10; 1Cr 12:28, 29; 14:29, 32, 37; Eph 2:20; 3:5; 4:11;
(e) of "Christ, as the aforepromised Prophet," e.g., Jhn 1:21; 6:14; 7:40; Act 3:22; 7:37, or, without the article, and, without reference to the Old Testament, Mar 6:15, Luk 7:16; in Luk 24:19 it is used with aner, "a man;" Jhn 4:19; 9:17;
(f) of "two witnesses" yet to be raised up for special purposes, Rev 11:10, 18;
(g) of "the Cretan poet Epimenides," Tts 1:12;
(h) by metonymy, of "the writings of prophets," e.g., Luk 24:27; Act 8:28.
| 2 | Strong's Number: g5578 | Greek: pseudoprophetes |
Prophet:
"a false prophet," is used of such
(a) in OT times, Luk 6:26; 2Pe 2:1;
(b) in the present period since Pentecost, Mat 7:15; 24:11, 24; Mar 13:22; Act 13:6; 1Jo 4:1;
(c) with reference to a false "prophet" destined to arise as the supporter of the "Beast" at the close of this age, Rev 16:13; 19:20; 20:10 (himself described as "another beast," Rev 13:11).
Prophet:
The ordinary Hebrew word for prophet is nabi, derived from a verb signifying "to bubble forth" like a fountain; hence the word means one who announces or pours forth the declarations of God. The English word comes from the Greek prophetes (profetes) which signifies in classical Greek one who speaks for another, especially one who speaks for a god, and so interprets his will to man; hence its essential meaning is "an interpreter." The use of the word in its modern sense as "one who predicts" is post‐classical. The larger sense of interpretation has not, however, been lost. In fact the English word prophet, has always been used in a larger and closer sense. The different meanings or shades of meanings in which the abstract noun is employed in Scripture have been drawn out by Locke as follows: "Prophecy comprehends three things: prediction; singing by the dictate of the Spirit; and understanding and explaining the mysterious, hidden sense of Scripture by an immediate illumination and motion of the Spirit."
Order and office.-The sacerdotal order was originally the instrument by which the members of the Jewish theocracy were taught and governed in things spiritual. Teaching by act and teaching by word were alike their task. But during the time of the judges, the priesthood sank into a state of degeneracy, and the people were no longer affected by the acted lessons of the ceremonial service. They required less enigmatic warnings and exhortations, under these circumstances a new moral power was evoked the Prophetic Order. Samuel himself Levite of the family of Kohath (1 Chronicles 6:28) and almost certainly a priest, was the instrument used at once for effecting a reform in the sacerdotal order (1 Chronicles 9:22) and for giving to the prophets a position of importance which they had never before held. Nevertheless it is not to be supposed that Samuel created the prophetic order as a new thing before unknown. The germs both of the prophetic and of the regal order are found in the law as given to the Israelites by Moses (Deuteronomy 13:1; 18:20; 17:18) but they were not yet developed, because there was not yet the demand for them. Samuel took measures to make his work of restoration permanent as well as effective for the moment. For this purpose he instituted companies or colleges of prophets. One we find in his lifetime at Ramah (1 Samuel 19:19, 20) others afterward at Bethel (2 Kings 2:3) Jericho (2 Kings 2:2; 2:5) Gilgal; (2 Kings 4:38) and elsewhere (2 Kings 6:1). Their constitution and object was similar to those of theological colleges. Into them were gathered promising students, and here they were trained for the office which they were afterward destined to fulfill. So successful were these institutions that from the time of Samuel to the closing of the canon of the Old Testament there seems never to have been wanting due supply of men to keep up the line of official prophets. Their chief subject of study was, no doubt, the law and its interpretation; oral, as distinct from symbolical, teaching being thenceforward tacitly transferred from the priestly to the prophetic order. Subsidiary subjects of instruction were music and sacred poetry, both of which had been connected with prophecy from the time of Moses (Exodus 15:20) and the judges (Judges 4:4; 5:1). But to belong to the prophetic order and to possess the prophetic gift are not convertible terms. Generally, the inspired prophet came from the college of prophets, and belonged to prophetic order; but this was not always the case. Thus Amos though called to the prophetic office did not belong to the prophetic order (Amos 7:14). The sixteen prophets whose books are in the canon have that place of honor because they were endowed with the prophetic gift as well as ordinarily (so far as we know) belonging to the prophetic order.
Characteristics.-What then are the characteristics of the sixteen prophets thus called and commissioned and entrusted with the messages of God to his people?
(1.) They were the national poets of Judea.
(2.) They were annalists and historians. A great portion of Isaiah, of Jeremiah, of Daniel, of Jonah, of Haggai, is direct or in direct history.
(3.) They were preachers of patriotism,-their patriotism being founded on the religious motive.
(4.) They were preachers of morals and of spiritual religion. The system of morals put forward by the prophets, if not higher or sterner or purer than that of the law, is more plainly declared, and with greater, because now more needed, vehemence of diction.
(5.) They were extraordinary but yet authorized exponents of the law.
(6.) They held a pastoral or quasi‐pastoral office.
(7.) They were a political power in the state.
(8.) But the prophets were something more than national poets and annalists, preachers of patriotism moral teachers, exponents of the law, pastors and politicians. Their most essential characteristic is that they were instruments of revealing God's will to man, as in other ways, so specially by predicting future events, and in particular foretelling the incarnation of the Lord Jesus Christ and the redemption effected by him. We have a series of prophecies which are so applicable to the person and earthly life of Jesus Christ as to be thereby shown to have been designed to apply to him. And if they were designed to apply to him, prophetical prediction is proved. Objections have, been urged. We notice only one, vis., vagueness. It has been said that the prophecies are too darkly and vaguely worded to be proved predictive by the events which they are alleged to foretell. But to this might be answered,
(9.) That God never forces men to believe, but that there is such a union of definiteness and vagueness in the prophecies as to enable those who are willing to discover the truth, while the willfully blind are not forcibly constrained to see it.
(10.) That, had the prophecies been couched in the form of direct declarations, their fulfillment would have thereby been rendered impossible or at least capable of frustration.
(11.) That the effect of prophecy would have been far less beneficial to believers, as being less adapted to keep them in a state of constant expectation.
(12.) That the Messiah of revelation could not be so clearly portrayed in His varied character as God and man, as prophet, priest and king, if He had been the mere teacher."
(13.) That the state of the prophets, at the time of receiving the divine revelation, was such as necessarily to make their predictions fragmentary, figurative, and abstracted from the relations of time.
(14.) That some portions of the prophecies were intended to be of double application, and some portions to be understood only on their fulfillment (compare John 14:29; Ezekiel 36:33).
HOW THE PROPHETIC GIFT WAS RECEIVED
We learn from Holy Scripture that it was by the agency of the Spirit of God that the prophets received the divine communication; but the means by which the divine Spirit communicated with the human spirit, and the conditions of the latter under which the divine communications were received, have not been clearly declared to us. They are however, indicated. In Numbers 12:6-8 we have an exhaustive division of the different ways in which the revelations of God are made to man.
(1.) Direct declaration and manifestation: "I will speak mouth to mouth, apparently, and the similitude of the Lord shall he behold."
(2.) Vision.
(3.) Dream, though it must be allowed that Scripture language seems to point out the state of dream and of trance or ecstasy, as a condition in which the human instrument received the divine communications, it does not follow that all the prophetic revelations were thus made. Had the prophets a full knowledge of that which they predicted? It follows from what we have already said that they had not, and could not have. They were the "spokesmen" of God (Exodus 7:1) the "mouth" by which His words were uttered, or they were enabled to view and empowered to describe pictures. Presented to their spiritual intuition; but there are no grounds for believing that, contemporaneously with this miracle, there was wrought another miracle, enlarging the understanding of the prophet so as to grasp the whole of the divine counsels which he was gazing into, or which he was the instrument of enunciating.
Names.-Of the sixteen prophets, four are usually called the great prophets, namely, Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel and Daniel, and twelve the Minor prophets, namely, Hosea, Joel, Amos, Obadiah, Jonah, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephaniah, Haggai, Zechariah and Malachi. They may be divided into four groups: the prophets of the northern kingdom-Hosea, Amos, Joel, Jonah; the prophets of the southern kingdom-Isaiah, Jeremiah, Obadiah, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephaniah; the prophets of the captivity-Ezekiel and Daniel; the prophets of the return-Haggai, Zechariah, Malachi. They may be arranged in the following chronological order, namely, Joel, Jonah, Hoses, Amos, Isaiah, Micah, Nahum, Zephaniah, Habakkuk, Obadiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel, Daniel, Haggai, Zechariah, Malachi.
Use of prophecy.-Predictive prophecy is at once a part and an evidence of revelation; at the time that it is delivered and until its fulfillment, a part; after it has been fulfilled, an evidence. As an evidence, fulfilled prophecy is as satisfactory as anything can be; for who can know the future except the Ruler who disposes future events? and from whom can come prediction except from Him who knows the future?
Development of Messianic prophecy.-Prediction, in the shape of promise and threatening, begins with the book of Genesis. Immediately upon the Fall, hopes of recovery and salvation are held out, but the manner in which this salvation is to be effected is left altogether indefinite. All that is at first declared is that it shall come through a child of woman (Genesis 3:15). By degrees the area is limited: it is to come through the family of Shem (Genesis 9:26) through the family of Abraham (Genesis 12:3) of Isaac (Genesis 25:18) of Jacob (Genesis 28:14) of Judah (Genesis 49:10). Balaam seems to say that it will be wrought by a warlike Israelitish King (Numbers 24:17). Jacob, by a peaceful Ruler of the earth (Genesis 49:10). Moses, by a Prophet like himself, i.e. a revealer of a new religious dispensation (Deuteronomy 15:15). Nathan's announcement (2 Samuel 7:16) determines further that the salvation is to come through the house of David, and through a descendant of David who shall be himself a king. This promise is developed by David himself in the Messianic psalms. Between Solomon and Hezekiah intervened some two hundred years, during which the voice of prophecy was silent. The Messianic conception entertained at this time by the Jews might have been that of a King of the royal house of David who would arise and gather under his peaceful sceptre his own people and strangers. Sufficient allusion to his prophetical and priestly offices had been made to create thoughtful consideration, but as yet there was, no clear delineation of him in these characters. It was reserved for the prophets to bring out these features more distinctly. In this great period of prophetism there is no longer any chronological development of Messianic prophecy, as in the earlier period previous to Solomon. Each prophet adds a feature, one more, another less clearly combine the feature, and we have the portrait; but it does not grow gradually and perceptibly under the hands of the several artists. Its culminating point is found in the prophecy contained in Isaiah 52:13-15 and 53.
Prophets of the New Testament.-So far as their predictive powers are concerned, the Old Testament prophets find their New Testament counterpart in the writer of the Apocalypse; but in their general character, as specially illumined revealers of God's will, their counterpart will rather be found, first in the great Prophet of the Church and his forerunner, John the Baptist, and next in all those persons who were endowed with the extraordinary gifts of the Spirit in the apostolic age, the speakers with tongues and the interpreters of tongues, the prophets and the discerners of spirits, the teachers and workers of miracles (1 Corinthians 12:10; 12:28). That predictive powers did occasionally exist in the New Testament prophets is proved by the case of Agabus (Acts 11:23) but this was not their characteristic. The prophets of the New Testament were supernaturally illuminated expounders and preachers.
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
