
















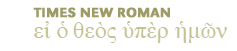
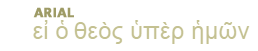

Stork:
Heb. hasidah, meaning "kindness," indicating thus the character of the bird, which is noted for its affection for its young. It is in the list of birds forbidden to be eaten by the Levitical law (Lev 11:19; Deu 14:18). It is like the crane, but larger in size. Two species are found in Palestine, the white, which are dispersed in pairs over the whole country; and the black, which live in marshy places and in great flocks. They migrate to Palestine periodically (about the 22nd of March). Jeremiah alludes to this (Jer 8:7). At the appointed time they return with unerring sagacity to their old haunts, and re-occupy their old nests. "There is a well-authenticated account of the devotion of a stork which, at the burning of the town of Delft, after repeated and unsuccessful attempts to carry off her young, chose rather to remain and perish with them than leave them to their fate. Well might the Romans call it the pia avis!"
In Job 39:13 (A.V.), instead of the expression "or wings and feathers unto the ostrich" (marg., "the feathers of the stork and ostrich"), the Revised Version has "are her pinions and feathers kindly" (marg., instead of "kindly," reads "like the stork's"). The object of this somewhat obscure verse seems to be to point out a contrast between the stork, as distinguished for her affection for her young, and the ostrich, as distinguished for her indifference.
Zechariah (Zec 5:9) alludes to the beauty and power of the stork's wings.
Stork:
stork (chacidhah; variously rendered in the Septuagint: Le 11:19, erodios; De 14:18, pelekan; Job 39:13, hasida (transliteration of Hebrew); Zec 5:9, (epops; Latin Ciconia alba): A large wading bird of the family Ardeidae, related to crane, ibis, heron and bittern. The stork on wing is a bird of exquisite beauty. The primary, secondary and a few of the tertiary wing feathers are black, the remainder, also the head, neck, and back and under parts white, the bill and legs red. When a perching white bird suddenly unfolds these wonderful wings, having at times a sweep of 7 ft., and sails away, it makes a very imposing picture. Zechariah in a vision saw a woman having the wings of a stork; Zec 5:9, "Then lifted I up mine eyes, and saw, and, behold, there came forth two women, and the wind was in their wings; now they had wings like the wings of a stork; and they lifted up the ephah between eaxth and heaven." These birds winter in Africa. In their spring migration many pairs pause in Palestine, others cross the Mediterranean and spread over the housetops, ruins and suitable building-places of Europe as far north as Rolland and England. Always and everywhere the bird has been more or less protected on account of its fidelity to a chosen location, its fearlessness of man and the tender love between mated pairs and for its young.
The stork first appears among the birds of abomination, and it is peculiar that the crane does not, for they are closely related. But the crane eats moles, mice, lizards and smaller animals it can capture, also frogs and fish. To this same diet the stork adds carrion and other offensive matter, and the laws of Moses, as a rule, are formulated with good reason. Yet at one time, storks must have been eaten, for Pliny quoted Cornelius Nepos, who died in the days of Augustus Caesar, as saying that "in his time storks were holden for a better dish at board than cranes." Pliny adds: "Yet see, how in our age now, no man will touch a stork if it be set before him on the board, but everyone is ready to reach into the crane and no dish is more in request." He also wrote that it was a capital crime in Thessaly to kill storks, because of their work in slaying serpents. This may have been the beginning of the present laws protecting the bird, reinforced by the steady growth of respect and love for its tender, gentle disposition. The Hebrew word chaidhah, from which the stork took its name, means "kindness."
There is a smaller stork having a black neck and back, that homes in Palestine, but only in small numbers as compared with the white. These birds flock and live in forests around the borders of waste and desert places, and build in trees. The young of both species remain a long time in the nest and are tenderly cared for, so much so indeed that from their performances and love of building on housetops arose the popular tradition that the stork delivers newly born children to homes. The birds first appear in Le 11:19 and De 14:18. Jeremiah noticed that the stork was migratory; see 8:7: "Yea, the stork in the heavens knoweth her appointed times; and the turtle-dove and the swallow and the crane observe the time of their coming; but my people know not the law of Yahweh." The Psalmist referred to their nesting in the cedars of Lebanon, for in Palestine these birds could not build on housetops, which were flat, devoid of chimneys and much used by the people as we use a veranda today; see Ps 104:17:
"Where the birds make their nests:
As for the stork, the fir-trees are her house."
Written by Gene Stratton-Porter
Stork:
(Heb. chasidah) a large bird of passage of the heron family. The of the largest and most conspicuous of land birds, standing nearly four feet high, the jet black of its wings and its bright red beak and legs contrasting finely with the pure white of its plumage (Zechariah 6:9). In the neighborhood of man it devours readily all kinds of offal and garbage. For this reason, doubtless it is placed in the list of unclean birds by the Mosaic law (Leviticus 11:19; 14:18). The range of the white stork extends over the whole of Europe, except the British isles, where it is now a rare visitant, and over northern Africa and Asia as far at least as Burmah. The black stork (Ciconia nigra, Linn.) though less abundant in places, is scarcely less widely distributed, but has a more easterly range than its congener. Both species are very numerous in Palestine. While the black stork is never found about buildings, but prefers marshy places in forests and breeds on the tops of the loftiest trees, the white stork attaches itself to man and for the service which it renders in the destruction of reptiles and the removal of offal has been repaid from the earliest times by protection and reverence. The derivation of chasidah (from chesed, "kindness") points to the paternal and filial attachment of which the stork seems to have been a type among the Hebrews no less than the Greeks and Romans. It was believed that the young repaid the care of their parents by attaching themselves to them for life, and tending them in old age. That the parental attachment of the stork is very strong has been proved on many occasions. Few migratory birds are more punctual to the time of their reappearance than the white stork. The stork has no note, and the only sound it emits is that caused by the sudden snapping of its long mandibles.
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
