
















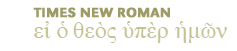
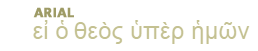

Magic:
The Jews seem early to have consulted the teraphim (q.v.) for oracular answers (Jdg 18:5,6; Zec 10:2). There is a remarkable illustration of this divining by teraphim in Ezek. 21:19-22. We read also of the divining cup of Joseph (Gen 44:5). The magicians of Egypt are frequently referred to in the history of the Exodus. Magic was an inherent part of the ancient Egyptian religion, and entered largely into their daily life.
All magical arts were distinctly prohibited under penalty of death in the Mosaic law. The Jews were commanded not to learn the "abomination" of the people of the Promised Land (Lev 19:31; Deu 18:9-14). The history of Saul's consulting the witch of Endor (1Sa 28:3-20) gives no warrant for attributing supernatural power to magicians. From the first the witch is here only a bystander. The practice of magic lingered among the people till after the Captivity, when they gradually abandoned it.
It is not much referred to in the New Testament. The Magi mentioned in Mat 2:1-12 were not magicians in the ordinary sense of the word. They belonged to a religious caste, the followers of Zoroaster, the astrologers of the East. Simon, a magician, was found by Philip at Samaria (Act 8:9-24); and Paul and Barnabas encountered Elymas, a Jewish sorcerer, at Paphos (13:6-12). At Ephesus there was a great destruction of magical books (Act 19:18,19).
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
